Reference Architecture for Agentic AI Systems
Use this layered checklist to move from user touchpoints to governance concerns without hunting across multiple diagrams—each section links directly to adjacent agentic references for deeper dives.
Why This Architecture Matters
The reference architecture of agentic LLM-based AI systems combines various components to enable autonomy, intentionality, proactivity, decision-making, self-regulation, and continuous learning. Here is a high-level overview of such architecture:
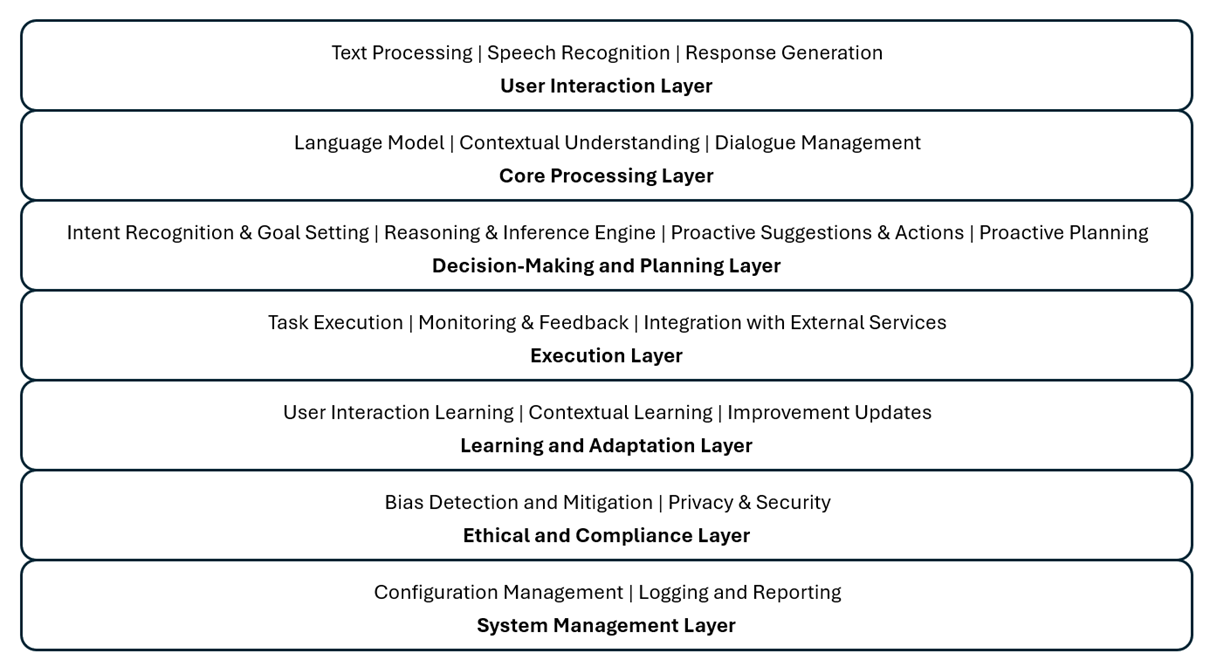
1. User Interaction Layer
- Natural Language Processing Interface
- Speech Recognition: Converts spoken language into text.
- Text Processing: Handles textual input from users.
- Natural Language Generation (NLG)
- Response Generation: Produces human-like text or speech output.
2. Core Processing Layer
- Language Model
- Contextual Understanding: Utilizes pre-trained language models (e.g., GPT-4) to understand context, intent, and user queries.
- Knowledge Base Integration: Enhances LLM output with domain-specific knowledge.
- Dialogue Management
- Context Management: Maintains conversation context across multiple interactions.
- Dialogue Flow Control: Manages progression so conversations stay coherent.
3. Decision-Making and Planning Layer
- Intent Recognition and Goal Setting
- Intent Detection: Identifies user intent from input.
- Goal Management: Sets and tracks goals based on user input and context.
- Reasoning and Inference Engine
- Decision Algorithms: Applies rule-based or machine learning logic to make decisions.
- Inference Mechanisms: Draws logical conclusions from available data.
- Proactive Planning Module
- Scenario Analysis: Predicts future states and plans actions accordingly.
- Proactive Suggestions: Offers proactive recommendations and actions.
4. Execution Layer
- Task Execution
- Action Management: Manages and executes actions to fulfill user requests.
- Integration with External Services: Interfaces with APIs and external systems to perform tasks (e.g., setting reminders, fetching information).
- Monitoring and Feedback
- Performance Monitoring: Tracks effectiveness and efficiency of task execution.
- User Feedback Collection: Gathers user feedback for continuous improvement.
5. Learning and Adaptation Layer
Cross-reference the deeper treatment of this layer in Learning and Adaptation.
- Continuous Learning Module
- User Interaction Learning: Learns from user interactions to improve responses and actions.
- Contextual Learning: Adapts to new contexts and information dynamically.
- Feedback Loop
- Error Analysis: Identifies and learns from errors in interactions.
- Improvement Updates: Updates models and algorithms based on feedback and new data.
6. Ethical and Compliance Layer
- Bias Detection and Mitigation
- Fairness Algorithms: Ensures decisions and actions are fair and unbiased.
- Regular Audits: Conducts regular audits to detect and mitigate biases.
- Privacy and Security
- Data Protection Mechanisms: Ensures user data privacy and compliance with regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
- Secure Communication: Secures data transmission and storage.
7. System Management Layer
- Configuration Management
- System Configuration: Manages configuration settings and preferences.
- Logging and Reporting
- Activity Logs: Maintains logs of user interactions and system actions.
- Reporting Tools: Generates reports on system performance and user interactions.
Conclusion
The reference architecture of agentic LLM-based AI systems integrates multiple layers and components to create a comprehensive, autonomous, and adaptive system. This architecture supports complex interactions, autonomous decision-making, proactive behavior, and continuous learning, all while ensuring ethical standards and user data protection.