The Evolution of Machine Learning Models: From LLMs to Action Models
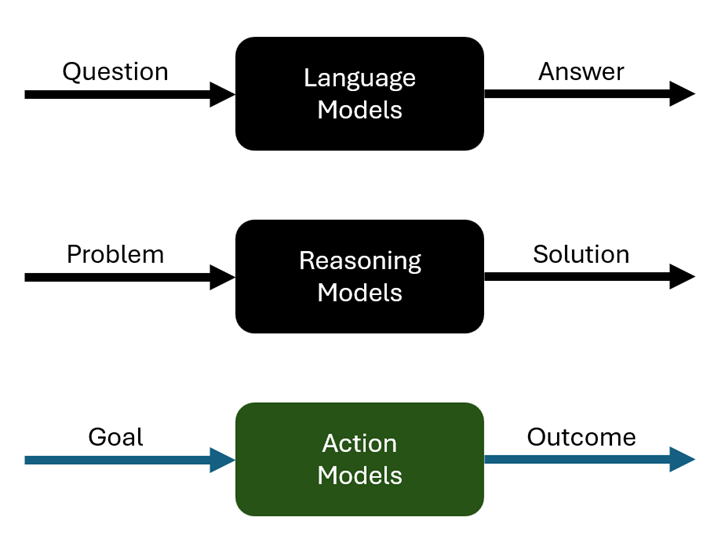
Machine learning has seen transformative changes in recent years, driven by the development of new categories of models. Large language models (LLMs) have significantly influenced natural language processing (NLP), followed by the emergence of reasoning models, which excel at handling more complex tasks. Now, we stand on the brink of a new frontier: action models. These models promise to extend the capabilities of their predecessors by interacting with the external world, taking meaningful actions, and seamlessly integrating into users' lives. In this article, we explore this progression in depth, examining the capabilities, challenges, and transformative potential of action models.
The Rise of Large Language Models (LLMs)
LLMs represent a groundbreaking leap in the field of NLP. Based on transformer architectures, these models are trained on massive datasets, enabling them to generate text that is coherent, contextually relevant, and human-like. Their widespread adoption has revolutionized multiple domains, pushing the boundaries of what artificial intelligence can achieve in processing and generating human language.
Key Contributions of LLMs:
- Chatbots: LLMs have powered conversational agents capable of understanding user input and providing helpful, context-aware responses. From customer support systems to personal virtual assistants, chatbots have benefited immensely from the contextual depth that LLMs provide.
- Language Translation: Services like Google Translate have incorporated LLMs to improve the quality and fluency of translations. By grasping subtle nuances in language, LLMs ensure more accurate and context-sensitive outputs.
- Text Generation: From creative writing and content summarization to drafting emails and legal documents, LLMs have showcased their ability to assist in a variety of content generation tasks, democratizing access to high-quality written communication.
However, despite their transformative capabilities, LLMs have limitations. While adept at understanding and generating text, they struggle with tasks requiring advanced reasoning, deep contextual understanding over extended text, or iterative problem-solving. This gap led to the emergence of reasoning models, the next step in the machine learning evolution.
Reasoning Models: The Next Logical Step
To address the limitations of LLMs, reasoning models were developed to handle more complex cognitive tasks. These models build on the foundational capabilities of LLMs while incorporating features that enable them to perform tasks requiring deeper thought and contextual understanding.
Defining Features of Reasoning Models:
- Handling Larger Contexts: Reasoning models excel at processing and retaining larger amounts of information. This allows them to operate on tasks requiring deep contextual understanding over multiple layers of complexity.
- Solving Challenging Problems: These models are adept at tackling complex math, science, and logical reasoning problems. By iterating over problems multiple times, they refine their outputs to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Allocating Computational Resources: Reasoning models intelligently allocate additional computational resources to harder tasks. This enables them to spend more time on challenging problems, producing well-thought-out solutions that were previously beyond the capabilities of earlier models.
Examples of Reasoning Models:
OpenAI's o1 models are a prime example, showcasing improved reasoning capabilities compared to traditional LLMs. The soon-to-be-released o3 models are expected to set new benchmarks in problem-solving and advanced reasoning. Despite these advancements, reasoning models remain largely confined to generating and processing information, lacking the ability to interact directly with the external world.
Enter Action Models: A Seamless Future
The natural progression from reasoning models is the development of models that can take actions based on user-defined goals. Action models promise to be a game-changer by integrating the generative and reasoning capabilities of previous models with the ability to perform tasks in the real world. These models represent a shift from passively processing information to actively achieving user goals.
What Are Action Models?
Action models are an emerging category of machine learning systems designed to:
- Connect with External Services: Unlike current models, which operate in isolation, action models will integrate with external AI-native services. This allows them to perform tasks such as booking flights, scheduling appointments, or managing finances.
- Take User-Defined Actions: Users will be able to define high-level goals, and the action model will autonomously plan and execute steps to achieve those goals. For example, organizing a holiday, managing budgets, or planning events could be entirely handled by these systems.
- Iterate and Negotiate: Action models will engage in continuous feedback loops with the user, refining their actions and negotiating with external services to deliver optimal outcomes.
- Plan and Orchestrate Steps: Action models will differ from current agents built on LLMs and reasoning models by incorporating planning and orchestration of steps as a core capability. This means they can autonomously manage multi-step tasks, ensuring seamless execution.
A Practical Example of Action Models in Use
Imagine a user who wants to plan a holiday based on specific preferences. An action model could:
- Gather Information: Initiate a conversation with the user to understand their budget, preferred destinations, travel dates, and desired experiences.
- Research Options: Connect to AI-native travel platforms to explore available flights, accommodations, and activities that align with the user's preferences.
- Negotiate and Optimize: Communicate with various services to secure the best deals and schedules, potentially even bundling offers for maximum value.
- Keep the User Informed: Provide real-time updates, suggest alternatives, and finalize bookings only after receiving the user's approval.
The result is a seamless, hands-free experience, transforming the way users interact with AI systems and significantly reducing the manual effort required to achieve complex goals.
Challenges in Building Action Models
While the potential of action models is immense, their development poses significant challenges that must be addressed to make them a practical reality.
Key Challenges:
- Integration with External Services: Action models will need to work with a variety of AI-native services designed for seamless integration. Scraping data from traditional websites will not suffice, as robust APIs and infrastructure will be required to support advanced interactions.
- Security and Privacy: Granting models the ability to take actions on behalf of users raises concerns about data security and potential misuse. Safeguards must be implemented to ensure privacy and prevent unauthorized access.
- Ethical Considerations: Developers must address ethical questions, such as ensuring transparency in decision-making, avoiding bias, and preventing unintended consequences resulting from autonomous actions.
- Technical Complexity: Creating models that reliably interact with dynamic external systems requires significant advances in architecture, error-handling, and dynamic adaptability. Ensuring seamless orchestration of multi-step processes will require unprecedented technical sophistication.
The Road Ahead
The journey from LLMs to action models reflects the natural evolution of machine learning, driven by the desire to create systems that are not only intelligent but also capable of meaningful interaction with the world. As we look to the future, several steps will be critical in realizing the potential of action models:
- Develop AI-Native Ecosystems: Building a robust ecosystem of AI-native services is a prerequisite for action models to thrive. This includes creating platforms designed for seamless API integration and real-time data sharing.
- Enhance Model Capabilities: Continuous improvements in reasoning, contextual understanding, and decision-making will be necessary to make action models more robust and reliable.
- Address Ethical and Practical Challenges: Collaboration among researchers, developers, and policymakers will be vital to ensure the responsible development and deployment of action models, addressing security, privacy, and transparency concerns.
- Foster User Trust: Ensuring users feel confident granting action models the authority to perform tasks on their behalf will be crucial. This will require clear communication, error handling, and user-friendly interfaces.
Conclusion
Action models represent a bold and exciting vision for the future of AI. By bridging the gap between understanding and action, they have the potential to revolutionize industries, enhance user experiences, and redefine the role of AI in our lives. While challenges abound, the promise of these models is too great to ignore. As AI continues to evolve, action models will not only transform the way we interact with technology but also redefine how technology serves humanity. The question is no longer whether action models will become a reality, but how soon we can bring them to life.